Accurate Future Value Calculator
Introduction to Future Value and the Future Value Calculator
The value of money changes over time. What a dollar buys today is not what it will buy in the future. What the dollar buys in the future is its future value. A future value calculator is a tool that calculates the dollar’s future value.
Two factors affect the dollar’s FV (and any other currency’s FV):
- Inflation (or deflation)
- Investment rate of return
The higher the inflation rate, the less the dollar will buy. The higher the investment rate of return (or interest rate)—or the greater the rate of deflation—the more the dollar will buy.
This future value calculator calculates the FV of an amount or asset after an exact number of days. It supports any rate of return (tested up to 99% per year) for 12 compounding frequencies, plus simple interest.
Because this calculator is date-sensitive and supports multiple compounding options, it is suitable for calculating the balance of a debt if the debtor has made no payments. More details appear below the calculator…
The Calculator-Calculate the Future Value of an Amount
Información
More About Future Value
The future value calculator usually calculates a nominal future value. This means the calculated amount reflects investment gains or interest earned on the money. A nominal future value does not reflect the effect of inflation.
If you want to know the real future value, you can calculate it in one of two ways.
How Does Inflation Affect Future Value?
If you want to know the purchasing power of the original amount after inflation, subtract an estimated inflation rate from the annual interest rate. For example, if your annual interest rate is 4.5% per year and you estimate that inflation will average 2% per year, then instead of entering 4.5% as your rate of return, you would enter 2.5%. The calculated FV will represent the real future value.

This terminology can be misleading. Economists call this the real future value, but it is only an estimated real future value because we can only estimate the future rate of inflation.
However, the real future value is a more accurate measure than the nominal future value, which does not take inflation into account.
If you want to be explicitly compensated for inflation, add the inflation rate to the annual interest rate. For example, if someone owed you $2,000 for 5.5 years and agreed to compensate you for 2% inflation in addition to a 4% interest rate, then you would add the inflation rate to the rate of return.
The result reflects the effect of inflation. Another way to state this is: if an investor wants to earn a real 4.5% gain on an investment, how much must the investor also earn to offset the loss of value from inflation?
The future value calculator makes all of these calculations straightforward.
Future Value Equations
En esta sección:
Future Value Equation – Daily Compound Interest
Variables: PV = 10,000; R = 10%; d = 365; n = 730.
Definiciones de variables
- R
- Tipo de interés nominal anual.
- d
- Days in a year, typically 360 or 365.
- i
- Daily interest rate.
- PV
- Present value — the principal amount (initial investment).
- n
- Number of days in the term.
Calculation Steps Explained – Fig. 2
- What is the future value of $10,000 invested for two years with daily compounding at a 10% annual interest rate?
To calculate the future value (FV) of an investment with daily compounding, use the formula
FV = PV × (1 + i)n, wherei = R ÷ dandnis the number of days in the term:- Calculate the daily interest rate:
i = 0.10 ÷ 365 ≈ 0.0002739726027…. - Substitute the values into the formula:
FV = 10,000 × (1 + 0.0002739726027…)730. - Simplify the base:
1 + 0.0002739726027… ≈ 1.0002739726027…. - Raise the base to the 730th power:
(1.0002739726027…)730 ≈ 1.22136930164…. - Multiply by the principal:
10,000 × 1.22136930164… ≈ 12,213.69.
The investment grows to $12,213.69 after two years of daily compounding at a 10% annual interest rate.
- Calculate the daily interest rate:
Solución paso a paso – Fig. 2
i = 0.10 ÷ 365 ≈ 0.0002739726027…FV = 10,000 × (1 + 0.0002739726027…)730≈ 10,000 × (1.0002739726027…)730≈ 10,000 × 1.22136930164…≈ 12,213.69
Respuesta final
The final answer (FV) is approximately $12,213.69, of which $2,213.69 is interest (I).
Validate the calculator. Two-year daily compound interest.
| Present Value (PV): | 10.000,00 € |
|---|---|
| Tipo de interés anual: | 10.0% |
| Days: | <calculado> |
| Start Date: | |
| End Date: | |
| Compounding Frequency: | Diario |
| Days in a Year: | 365 |
| Valor futuro (VF): | = $12,213.69 |
| Gain on Investment (Interest Earned): | $2,213.69 |
Notas:
- Este ejemplo utiliza el mismo cálculo que se muestra en la Fig. 2.
- For daily compounding, the calculator always uses days as the time unit when calculating the term (n).
- You can either enter two dates that are exactly two years apart (the calculator will determine the number of days), or—
- Enter a specific number of days (e.g., 365 or 366 if February 29 is included), and the calculator will determine the end date.
Future Value – Daily Simple Interest
Variables: PV = 10,000; R = 10%; d = 365; n = 730 (two years).
Definiciones de variables
- R
- Tipo de interés nominal anual.
- d
- Number of days in a year (commonly 360 or 365).
- i
- Daily interest rate.
- PV
- Present value — the principal amount (initial investment).
- n
- Number of days in the investment term.
Calculation Steps Explained – Fig. 4
- What is the future value of an investment of $10,000 invested for two years with simple interest at a 10% annual interest rate?
To calculate the future value (FV) of this investment under daily simple interest, use the formula
FV = PV + PV × i × n, wherei = R ÷ dandnis the number of days in the term. The steps are:- Calculate the daily interest rate:
i = 0.10 ÷ 365 ≈ 0.0002739726027…. - Substitute the known values into the formula:
FV = 10,000 + 10,000 × 0.0002739726027… × 730. - Multiply the daily rate by the number of days:
0.0002739726027… × 730 ≈ 0.20000000000000…. - Multiply that result by the principal:
10,000 × 0.20000000000000… ≈ 2,000.00. - Add the interest to the original principal:
10,000 + 2,000.00 ≈ 12,000.00.
The investment grows to $12,000.00 after two years of daily simple interest at a 10% annual interest rate.
- Calculate the daily interest rate:
Solución paso a paso – Fig. 4
i = 0.10 ÷ 365 ≈ 0.0002739726027…FV = 10,000 + 10,000 × 0.0002739726027… × 730≈ 10,000 + 10,000 × 0.20000000000000…≈ 10,000 + 2,000.00FV ≈ 12,000.00
Respuesta final
The final answer (FV) is approximately $12,000.00, of which $2,000.00 is interest.
Validate the calculator. One-year, monthly-compounded interest.
| Present Value (PV): | 10.000,00 € |
|---|---|
| Tipo de interés anual: | 10.0% |
| Number of Days: | <calculated> |
| Start Date: | |
| End Date: | |
| Compounding Frequency: | Exact ÷ Simple |
| Days in a Year: | 365 |
| Valor futuro (VF): | $12,000.00 |
| Total Interest (Gain): | $2,000.00 |
Notas:
- Este ejemplo utiliza el mismo cálculo que se muestra en la Fig. 4.
- For simple interest, the calculator always measures time in days.
- You can either enter two dates exactly two years apart (the calculator will calculate the number of days), or—
Future Value Calculator Help
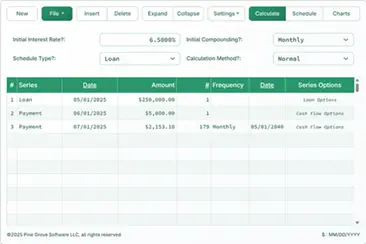
This calculator computes the future value (FV) of a single amount. Use the “future value schedule” feature if you want to calculate the future value of a series of investments or deposits.
Enter the present value (the amount invested) and the nominal annual interest rate.
Date Math: If you change either date, the calculator will determine the number of days. If you enter a positive number of days, the end date will update. If you enter a negative number of days, the start date will update.
This feature allows you to calculate FV for a specific number of days without needing to specify calendar dates. For example, if you want the FV after 31 days, enter “31” as the number of days. The specific start and end dates are not important.
Set the compounding method and the number of days in a year. Then click “Calc.” The calculator will display the future value (initial amount plus total interest).
The gain may be calculated based on a fixed unit of time, such as one month. In that case, the monthly gain is always the same for the same annual interest rate and the same principal balance, regardless of the actual length of the month. For example, with a principal of $10,000 and an annual interest rate of 6.75%, the monthly gain for February is the same as the monthly gain for March.
Tips for Entering Dates
Para establecer su moneda y formato de fecha preferidos, haga clic en el enlace “$ : MM/DD/YYYY” en la esquina inferior derecha de cualquier calculadora.
You may set a date either by clicking the calendar button [] or by typing 8 digits according to the selected date format.
If you are using the calendar: To quickly change to a new date, click the current month’s name at the top to open a list of months. Then click the year to open a list of years. Select the year, then the month, and finally the date. You can also click “Today” to select the current date.
If you are using the keyboard: Type only the 8 required digits. Do not type separators (“/” or “-”). When you tab to a date input or single-click it, the entire date will be selected. You can begin typing to overwrite it—there is no need to delete it first. Alternatively, press the right arrow key to clear the selection and use backspace to edit. Depending on the selected date format, you can backspace to clear the last two digits of the year and reenter them to change the year quickly.

Comments, suggestions & questions welcomed...